
| Thermodynamics > Entropy and the Second Law > Heat Cycles | DCS# 4F30.xx |

| air conditioner |
N002 |
| temperature probes |
101-05-D6 |
| laptop with LoggerPro 3 |
206 |
| IR camera | 206 |
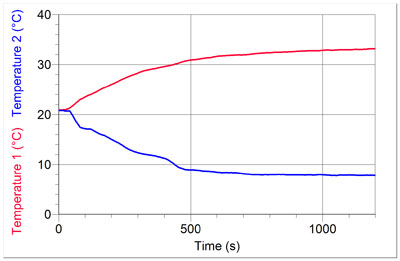
Display the hot and cold air temperatures with the computer-interfaced temperature probes and/or use the IR camera to show this.
The switch on the front panel should be set to bypass the thermostat and turn on the compressor regardless of the room temperature.
Start the air conditioner on "hi fan" mode before starting data collection, then switch to "hi cool" mode, otherwise data collection may stop when the fan motor starts. It may also stop when the compressor starts. In that case, it will be necessary to restart data collection or reconnect the LabPro.
The temperature data and the input power can be used to calculate the coefficient of performance:
Position the cold temperature probe so it is at the center of the left set of vents, where the airflow is most uniform.
The measured
flow rates (averaged readings of wind speed monitor x area of
vent or intake) with the fan on high
Manufacturer's information: 5100 BTU, 565 watts, 5.3 Amp, 9.0 EER. So the claimed COP is 0.293 x EER = 2.6
If you need to restart the air conditioner, wait three minutes before doing so or a breaker will trip.
Experiment file is "airconditioner". Or just plot the two temperatures at a rate of 1 sample/sec for 20 minutes, which is enough time for the temperatures to level off.